A major concern is the presence of breast cancer in underserved communities, including those
TOO YOUNG FOR A MAMMOGRAM. Whereby the medical community touts the recommended (and legal/billable status) of getting a mammo scan should be between 40-50, what happens to the many women who do not fit this age criteria? How would they even know to get checked without the support of their clinicians or an alarm from family history?
Decades into the battle against breast cancer, clinicians and the public are much more educated about EARLY DETECTION, PREVENTION and the current protocols and modalities available to save lives. Recent headlines on DENSE BREAST and the advancements in ULTRASOUND SCANNING supports a major part of this battle.
UNDERSERVED AGE FOR EARLY DETECTION
According to Breastcancer.org, "Where mammography is available, ultrasound should be seen as a supplemental test for women with dense breasts who do not meet high-risk criteria for screening [with] MRI and for high-risk women with dense breasts who are unable to tolerate MRI... but if mammography isn’t available, then ultrasound seems to be a good alternative for breast cancer screening."
A recent cohort study is underway under a partnership between Molloy College and
AreYouDense.org to publish new findings about low BMI patients and younger women about the presence of dense breast tissue. This same review also covers the advantages of ultrasound use where mammography is not available.
Mammography is the current standard for breast cancer early detection for women 40 & older. Recent studies have shown nearly half of all women who get mammograms are found to have dense breasts, exposing this population to the risk that mammograms may miss potentially cancerous tumors concealed by dense breast tissue. Dr. Cutter's initial concepts to target LOW BMI (bet 12-22% body fat) was personally inspired. As an active TRIATHLETE, her own diagnosis sparked her survey and inquiry throughout the athletic community where she uncovered a significant trend that became the basis for this research. She wishes to target younger women, athletes and members of underserved communities. "Younger women may be more likely to have dense breasts... also I find athletes with LOWER BMI (body mass index) or those with less body fat are more likely to have more dense breast tissue compared with women who are obese." (See complete feature article)
VIEWPOINT
WHAT ABOUT IF YOU'RE TOO YOUNG FOR A MAMMOGRAM? I went to my doctor for a lump I felt in my breast and she gave me a response that set off red flags: "don't worry about it". Being a researcher involved in breast density and breast cancer, I knew that I had to take action; I was fortunate enough to have my breast ultrasound training with Dr. Robert Bard (cancer imaging specialist, NYC) upcoming in the next week. Dr. Bard showed me how to use the ultrasound to help me find two benign tumors in my breasts, and it was there that he reported that I have dense breasts. Had I not taken action in getting screened at the young age of 22, I would have never known that I should be getting screened via ultrasound every 6 months (because having dense breasts puts me at a higher risk for breast cancer), nor would I have known that I had benign breast tumors.
- ALEXANDRA FIEDERLEIN, 22
Cancer Researcher/ Graduate- Molloy Univ.
NEWS FROM THE FIELD
The DENSE BREAST TISSUE / CANCER CONNECTION is a topic that has finally achieved proper recognition in our community. Thanks to organizations like The 'ARE YOU DENSE?' Foundation, awareness of this health concern has now shed light to the risk to 40+% of the national women's population whereby more clinicians are now recognizing the need to state a patient's dense breast status. Research crusaders like Dr. Noelle Cutter and research associate Alexandra Fiederlein from Molloy University are underway the 2022 National Survey of Dense Breast Studies by bringing ultrasound access to underserved members of the women's community.
In a recent episode of SPOTLIGHT ON AMERICA, Dr. Bard spoke as the clinical expert in the report "Millions of women have this breast cancer risk factors... why aren't they being informed?" -- TND REPORT/Spotlight on America is pressing to ensure women have access to a crucial health fact that could save their lives. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 40% of women have dense breast tissue, which is a risk factor for cancer. The TND team first highlighted this issue in October 2021, and more than a year later, we expose how some women are still being left in the dark about their density, and federal health bodies are failing to make sure they’re informed. |
2022 REVIEW ON WOMEN'S EARLY DETECTION STANDARDS
Breast cancer is still one of the most common cancers in women, and the leading cause of cancer mortality. While mammography is considered the standard imaging for early detection, it falls short for many – including those with dense breasts. Approximately 40% of women have dense breasts, which we now know is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. On top of this increased risk, mammogram is less sensitive for early detection – up to 50% less for women with the highest breast density. [1] As a result many women are not diagnosed until they have a much later stage cancer – and a worse prognosis. [2]
The State of Connecticut passed legislation requiring notification of breast density in 2009, after having passed legislation requiring insurance coverage for ultrasound for dense breasts in 2005. As an ObGyn physician practicing in CT at the time, I remember the discussions with colleagues and patients around this issue although at the time there were no formal efforts to raise awareness or update guidelines from our national specialty organization, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
PERSPECTIVE: PERSONAL FINDINGS BY A CLINICAL PROFESSIONALI was fortunate to have benefited personally from this effort when I had my first screening mammogram shortly after the law went into effect. The reading radiologist personally informed me of my high breast density immediately after the mammogram, and after recommending a breast ultrasound for further evaluation this was done right then and there. I walked away from my appointment feeling well informed, and any potential anxiety relieved by the prompt additional imaging and results. I also knew that I needed a different approach for my screenings going forward.
Between 2009 and 2019, 37 other states and D.C. passed legislation requiring notification of breast density, one of the last being my new home state of New Mexico. In 2019 a federal law was passed to require both clinician and patient reports contain plain language around the woman’s breast density, and to discuss with her provider. The FDA then created standard language that has now been implemented, requiring reporting on a woman’s individual breast density, and recommendation to discuss with her provider.

There is still much to be learned about what causes dense breasts and why women with dense breasts have an increased risk of breast cancer, and our ongoing study is one of many that are seeking to answer these questions at the molecular and genetic level. But the evidence that supplementing mammograms with other imaging modalities can increase the rate of early detection is substantial, and provides us with tools we can use right now to make a difference. [3,4] Despite this progress, there are still significant hurdles in changing the standard of care. A recent experience with my routine breast cancer screening highlighted the ongoing challenges. When I had asked to schedule an ultrasound with my screening mammogram, I was informed that it was not done this way – I could only get a mammogram. After my mammogram, I had to wait to receive my letter in the mail approximately one week later to be able to take any additional steps. The interpretation included a description of breast density and recommended to discuss any additional care with my physician.
When I called to schedule an ultrasound, I was told that since the radiologist did not recommend it in the report, I could not schedule it. I then had to speak with my primary care provider, educating her on dense breasts and why I needed an ultrasound. Luckily, she agreed to order one. While the radiology facility still questioned the order, eventually I was able to have this done. When the radiologist came in to discuss my results, she too was confused as to why I was having the ultrasound, and was not aware that this should be standard for women with dense breasts.
Fortunately all was fine, but had I not been a physician that was fully aware of this issue, I would very likely have had only a mammogram and walked away with a dangerously false sense of security. This experience highlighted for me how much still needed to be done more than 20 years after my first experience. Legislation is only part of the solution. Clinician education and public awareness are the keys to changing how the intention behind these laws gets translated into actual change in health care.
As I experienced, many clinicians are ill-informed about the nature of dense breasts, and options for adjunctive screening including ultrasound or MRI. This means that many of these reports end up being filed away with no further action being taken that could make a significant difference in early detection and saving lives.
EPILOGUE: CURRENT STANDARDS VS NEEDS
ACOG still officially does not recommend any further imaging for women with dense breasts on mammogram, despite the significant body of evidence suggesting that mammogram alone is insufficient and adjunctive imaging with ultrasound or MRI increases rate of early detection. [5] The U.S. Preventive Task Force [6] does not recommend routine adjunctive imaging for screening women with dense breasts. This leaves many healthcare practitioners, from ObGyns to other primary care providers, unprepared to discuss this with their patients or provide sound recommendations.
The American College of Radiologists, who also publishes the BIRADS standards for breast cancer screening, acknowledges awareness of breast density detection issues with mammography but stops short of recommending routine adjunctive imaging. Instead, they list ultrasound and MRI as “may be appropriate”. [7] We have enough evidence to know how to better serve women with dense breasts, and we can do better. Now we need to push for better education of all primary health care providers, including ObGyns, and continue to raise awareness for women around current knowledge and best practices.
References
1) Gordon PB. The Impact of Dense Breasts on the Stage of Breast Cancer at Diagnosis: A Review and Options for Supplemental Screening. Curr Oncol. 2022 May 17;29(5):3595-3636.
2) Chiu, S.Y.H.; Duffy, S.; Yen, A.M.F.; Tabár, L.; Smith, R.A.; Chen, H.H. Effect of baseline breast density on breast cancer incidence, stage, mortality, and screening parameters: 25-Year follow-up of a Swedish mammographic screening. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 1219–1228
3) Harada-Shoji N, Suzuki A, Ishida T, Zheng YF, Narikawa-Shiono Y, Sato-Tadano A, Ohta R, Ohuchi N. Evaluation of Adjunctive Ultrasonography for Breast Cancer Detection Among Women Aged 40-49 Years With Varying Breast Density Undergoing Screening Mammography: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Aug 2;4(8):e2121505
4) Mann, R.M., Athanasiou, A., Baltzer, P.A.T. et al. Breast cancer screening in women with extremely dense breasts recommendations of the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI). Eur Radiol 32, 4036–4045 (2022).
5) Management of Women With Dense Breasts Diagnosed by Mammography. ACOG Committee Opinion. CO Number 625 March 2015
6) https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/breast-cancer-screening
7) American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Supplemental Breast Cancer Screening Based on Breast Density. 2021

Feature: Diagnostic Tech Review/News:
TRACE4BDENSITY® − THE RADIOLOGISTS’ GUIDED ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE TOOL FOR THE AUTOMATIC DENSITY CLASSIFICATION OF MAMMOGRAMS
.jpg)
One relevant challenge in using mammographic breast density as a driver to supplemental screening with manual or automatic ultrasound, MRI, contrast-enhanced mammography, or other new diagnostic methods is the suboptimal reproducibility of visual classification into the four ACR (Americal College of Radiation) BI-RADS® categories. This is an important problem, especially considering that the last BI-RADS® manual does not base the breast density classification on a pure semiquantitative assessment of the fibrogladular to fatty tissue ratio but takes into consideration the possibility of a masking effect of also limited areas of dense tissue that may obscure underlying cancers. Therefore, artificial intelligence (AI) methods are the best candidate to mimic the qualitative human reading aiming at reducing the risk of a delayed cancer diagnosis, providing an immediate breast density classification with a 100% reproducibility.
DeepTrace Technologies SRL (http://www.deeptracetech.com/), the multi-awarded university spinoff of the IUSS School of Pavia, Italy, developed an AI software for automatic breast density classification using a deep learning approach, i.e., supervised convolutional neural networks: TRACE4BDensity®. The system was trained using the majority breast density category determined by seven board-certified radiologists who independently visually assessed 760 mediolateral oblique images. The model showed an accuracy of 89.3% in distinguishing BI-RADS a or b (nondense breasts) versus c or d (dense breasts) categories, with an agreement of 90.4% and a reliability of 0.807 (Cohen κ) compared with human readers. The clinical study that used TRACE4BDensity has been published in Radiology Artificial Intelligence 2022[1] and recently presented at the European Congress of Radiology in Vienna on July 16, 2022.
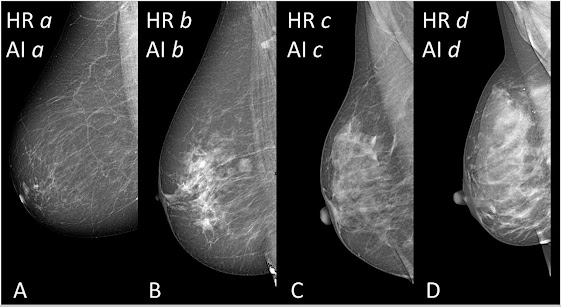
From A to D: examples of human readers (HR)–artificial intelligence (AI) agreement. TRACE4BDensity showed a 89.3% agreement and a reliability of 0.807 (Cohen κ) with human readings for the differention of dense breasts (category c or d) versus nondense breasts (category a or b). Radiol Artif Intell 2022 (doi/10.1148/ryai.210199).
The software can be directly applied to the PACS of radiology centers providing the breast density category in a few seconds with 100% reproducibility, allowing breast radiologists to overcome the limitations of human reading that unfortunately may give different answers to the crucial question: Are you dense? In addition, this approach can be considered more fitting with the aim of avoiding delayed cancer diagnoses than methods purely based on quantitative assessment of fibroglandular and fatty breast tissue that may underestimate the masking effect of localized high- density areas. Such an accurate tool, proposing a standardized density classification, represents a valid help in the decision-making process and in proposing a more personalized breast cancer screening. «TRACE4BDensity can help us to provide advice to women with dense breasts about the possibility of having, after a negative mammogram, additional screening with ultrasound, MRI, or contrast-enhanced mammography − explains Professor Francesco Sardanelli, head of the Diagnostic Imaging Service at the IRCCS Policlinico San Donato, coordinator of the Gruppo San Donato Breast Imaging Joint Research Unit, and full professor at the University of Milan, principal investigator of the study − This software, therefore, proves useful for radiologists as well as for women and patients».
References:
1) Development and Validation of an AI-driven Mammographic Breast Density Classification Tool Based on Radiologist Consensus, https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/ryai.210199
CONTRIBUTORS:
DR. ROBERT L. BARD has paved the way for the diagnostic study of various cancers both clinically and academically. He runs an active NYC practice (Bard Diagnostic Imaging) using the latest in digital Imaging technology which has been also used to help guide biopsies and, even replicate much of the same reports of a clinical invasive biopsy. Imaging solutions such as high-powered Sonograms, Spectral Doppler, sonofluoroscopy, 3D/4D Image Reconstruction and the Spectral Doppler are safe, noninvasive, and does not use ionizing radiation. His commitment to lead the community of cancer imaging and diagnostic experts has led to the establishment of the "Get Checked Now!" campaign.

JOSEPH J. CAPPELLO married Nancy Marcucci, in 1974 and the story began. Joe is the co-founder and executive director of Are You Dense, and Are You Dense Advocacy- in January of 2019 after Nancy’s passing from treatment related bone marrow cancer (MDS). His passion is to continue Nancy’s legacy by pursuing the goal that they set in 2004; that not one woman would die from a late stage breast cancer due to dense breast tissue. In 2009, Joe and Nancy championed the first in the nation breast density inform law in the State of Connecticut (and now, 36 States have breast density legislation).

ROBERTA KLINE, MD (Educational Dir. /Women's Diagnostic Group) is a board-certified ObGyn physician, Integrative Personalized Medicine expert, consultant, author, and educator whose mission is to change how we approach health and deliver healthcare. She helped to create the Integrative & Functional Medicine program for a family practice residency, has consulted with Sodexo to implement the first personalized nutrition menu for healthcare facilities, and serves as Education Director for several organizations including the Women’s Diagnostic Health Network, Mommies on a Mission.
Copyright Notice: The materials provided on this website/web-based article are copyrighted and the intellectual property of the publishers/producers (The NY Cancer Resource Alliance/IntermediaWorx inc. and The AngioFoundation). It is provided publicly strictly for informational purposes within non-commercial use and not for purposes of resale, distribution, public display or performance. Unless otherwise indicated on this web based page, sharing, re-posting, re-publishing of this work is strictly prohibited without due permission from the publishers. Also, certain content may be licensed from third-parties. The licenses for some of this Content may contain additional terms. When such Content licenses contain additional terms, we will make these terms available to you on those pages (which his incorporated herein by reference).The publishers/producers of this site and its contents such as videos, graphics, text, and other materials published are not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. For any questions you may have regarding a medical condition, please always seek the advice of your physician or a qualified health provider. Do not postpone or disregard any professional medical advice over something you may have seen or read on this website. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or 9-1-1 immediately. This website does not support, endorse or recommend any specific products, tests, physicians, procedures, treatment opinions or other information that may be mentioned on this site. Referencing any content or information seen or published in this website or shared by other visitors of this website is solely at your own risk. The publishers/producers of this Internet web site reserves the right, at its sole discretion, to modify, disable access to, or discontinue, temporarily or permanently, all or any part of this Internet web site or any information contained thereon without liability or notice to you.









.jpg)


.jpg)








No comments:
Post a Comment